Kailan (Brassica oleracea) -jennie-tang.jpg?sfvrsn=441f07e_3/brassica-oleracea-(alboglabra-group)-jennie-tang)
Photo credit: Jennie Tang
It has bluish green to dark green coloured leaves with thick stems that are smooth and pale green in colour. ‘Lan’ refers to blue in Chinese, which accurately describes its bluish coloured leaves. It is from the Alboglabra group.
Germination time: Three to five days
Harvest time: 21 to 55 days
Once these plants reach around 20 cm tall (10 cm for Nai Bai) or the desired size, you may harvest the edibles by uprooting the whole plant. Alternatively, you may use the cut-and-come again method to harvest for endless supply of vegetables (e.g. Kow Peck Chye, Huang Jin Bai Cai and Nai Bai etc).
Another indication to harvest your plant is when you spot flowering. Once the flower blooms, the vegetable might be over matured and a little too old for consumption. However, you may still eat the flower from the Nai Bai and Huang Jin Bai Cai.
Tips on Growing your Brassicas
- Prepare your plot by ensuring the soil is well-prepared with nitrogen-rich organic fertilisers.
- Raise seedling using the seed tray method to prevent overplanting, overcrowding, and damaging of root during transplanting.
- Space the seedling at 10 to 15 cm apart to ensure good air circulation with sufficient space for the plant to grow.
- Ensure that the plants received four to six hours of direct sunlight daily to grow well.
- To promote the growth of leaves, add fertiliser to your soil regularly to supply sufficient nitrogen (N).
a. Leafy vegetables need fertiliser high in nitrogen to grow more leaves.
b. Usually fertilise once every two weeks or follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
c. Use processed animal manure with high N content (e.g. chicken or goat pellets).
- Consider installing netting as a form of pest control to avoid insects like snails, grasshoppers and leaf miners.
a. Mechanical or physical control is one of the approaches for Integrated Pest Management. This involves the use of traps, screens or nets to prevent pest activity or to remove pests from an area.
- Harvest the plant roughly a month after germination or before it flowers. Otherwise, the leaves might be very tough to chew when the plant gets old.
If you are a gardening newbie, visit NParksSG, our refreshed YouTube Channel that serves as a one-stop repository for some 300 video resources. It covers topics ranging from types of soil needed for your garden and how to plant, harvest and even cook your edibles.
For more information about the flora and fauna found in Singapore, please visit Flora and Fauna Web.
If you like what you read, follow us on Facebook, Instagram and Telegram to get the latest updates.
Text by Teo Xin Ni
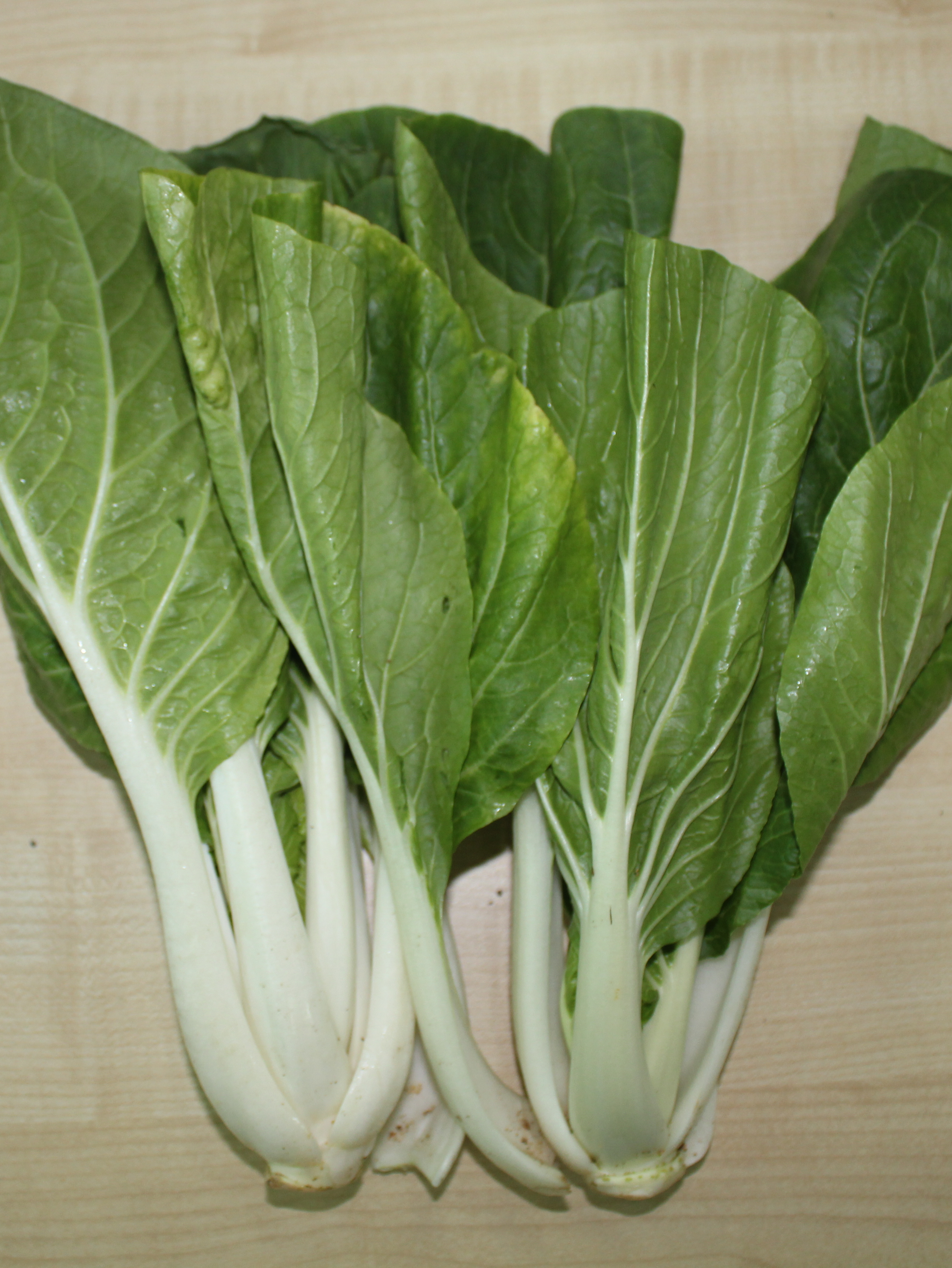





.jpg?sfvrsn=61c6f68d_3/brassica-rapa_huang-jing-bai-cai_vicky-lim-yen-ngoh-(4))
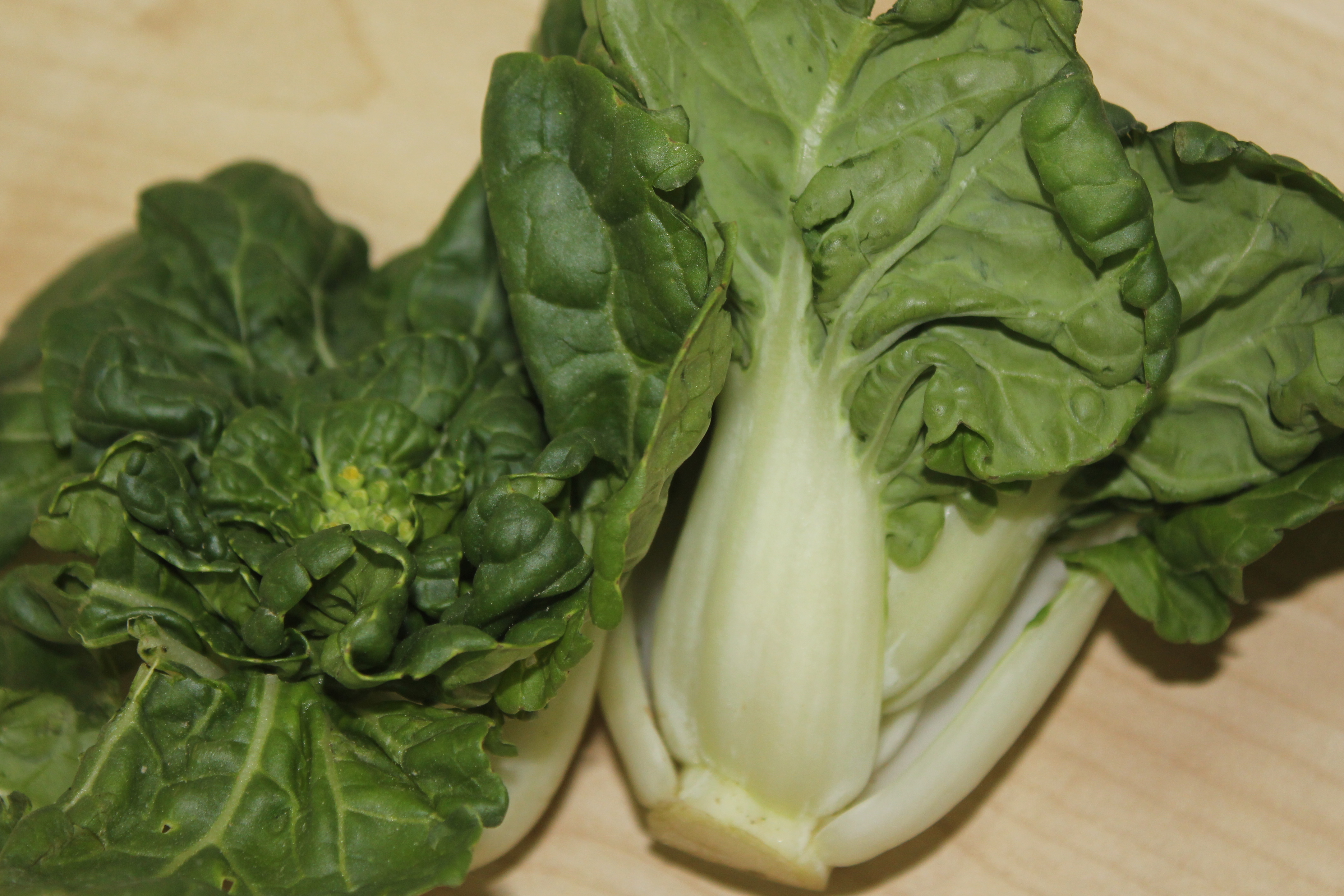

-jane-li.jpg?sfvrsn=6e947d75_3/brassica-rapa-(parachinensis-group)-jane-li)
-jennie-tang.jpg?sfvrsn=441f07e_3/brassica-oleracea-(alboglabra-group)-jennie-tang)