
Back
Garcinia atroviridis Griff. ex T.Anderson
| Family Name: | Clusiaceae (Guttiferae) |
| Common Name: | Asam Gelugor, Gelugor |
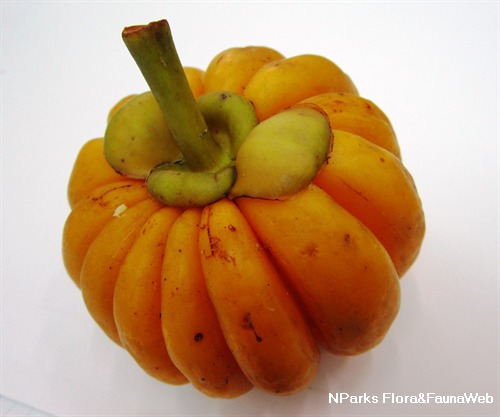
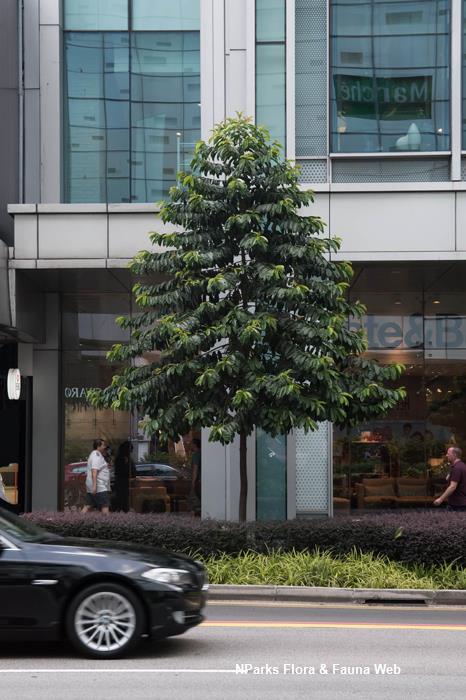
Garcinia atroviridis or Asam Gelugor is a native tree of Singapore. Growing to a height of 27 m tall, Asam Gelugor has a narrow conical crown with thick glossy foliage. It has bright red flowers produced singly (female flowers) or in clusters of 10 - 22 blooms (male flowers). The flower has 4 circular to broad-spoon like petals and a button-like stigma. The fruit is fleshy, bright yellow with deep ridges running along the fruit.
Name
Classifications and Characteristics
| Plant Division | Angiosperms (Flowering Seed Plants) (Dicotyledon) |
|---|---|
| Plant Growth Form | Tree (Medium (16m-30m)) |
| Lifespan (in Singapore) | Perennial |
| Mode of Nutrition | Autotrophic |
| Plant Shape | Conical |
| Maximum Height | 27 m |
Biogeography
| Native Distribution | India, Myanmar, Thailand, Peninsular Malaysia, and Singapore |
|---|---|
| Native Habitat | Terrestrial (Primary Rainforest, Secondary Rainforest) |
| Preferred Climate Zone | Tropical |
| Local Conservation Status | Native to Singapore (Critically Endangered (CR)) |
Description and Ethnobotany
| Growth Form | It is a medium sized, dioecious tree with a dense narrow conical crown that can grow to 27 m tall, bearing many slender drooping branches. |
|---|---|
| Foliage | Leaves are simple, leathery, glossy, narrowly oblong held on a winged stalk of up to 2.5 cm. Young leaves and petiole are red and turns green with time. The leaves measure 14 - 28 cm long, 4 - 8 cm wide, with fine dark wavy lines on the underside. |
| Flowers | Its large, faintly fragrant to scentless flowers are unisexual where the female and male flowers are borne on separate individuals. The flower consist of 4 large, fleshy, circular to broadly spoon-shaped petals and 4 unequal sepals, 4 - 5.5 cm wide. Male flowers are bright red, produced in clusters between 10 - 22, numerous stamens surround the sunken button-like stigma. The female flowers are often produced singly, rarely in pairs with a large flat red-brown button-like stigma, at the tip of the branches. |
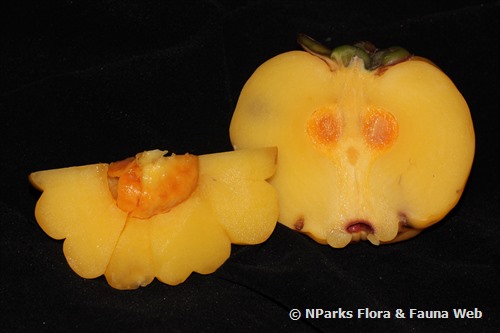
| Fruit | The fruit is fleshy and thick-walled, depressed globose with deep ridges along the fruit. The fruit held on a thick stalk of 2.5 cm wide, seated on persistent sepals and petals, starts off yellow and turns to bright yellow upon ripening. Each containing up to 16 seeds in sticky pale yellow latex. |
| Habitat | Occurs in tropical lowland evergreen rainforest, peat swamps forests and along streams, up to 550 m in altitude <1,2> |
| Associated Fauna | Its flowers are pollinated by insects. Its fruits are eaten by small mammals. |
| Cultivation | It can be propagated by seed. |
| Etymology | Latin Garcinia, commemorating after Laurent Garcin (1683-1751), a French botanist who travelled widely in India; Latin atroviridis, very dark green, referring to the colour of the leaves. |
| Ethnobotanical Uses | Edible Plant Parts : Edible Fruits, Edible Leaves Food (Fruit or Vegetable): The fresh fruits or dried fruit slices are used as a seasoning or sour relish (asam gelugor) in cooking, including curries. The young leaves are eaten. Medicinal: The juice from the leaves is used by a woman after childbirth. A decoction of the leaves and roots is used for ear-aches. When mixed with vinegar, the fruit is used in a lotion for a woman after confinement. |
Landscaping Features
| Landscaping | The plant has a sparse broken conical canopy, and new leaves that flush red. It is a tree suitable for gardens, parks and roadsides. |
|---|---|
| Desirable Plant Features | Ornamental Foliage, Ornamental Fruits, Ornamental Form |
| Landscape Uses | General, Suitable for Roadsides, Parks & Gardens, Small Gardens |
Fauna, Pollination and Dispersal
| Pollination Method(s) | Biotic (Fauna) |
|---|---|
| Seed or Spore Dispersal | Biotic (Fauna) |
Plant Care and Propagation
| Light Preference | Full Sun, Semi-Shade |
|---|---|
| Water Preference | Moderate Water |
| Plant Growth Rate | Moderate |
| Rootzone Tolerance | Moist Soils, Well-Drained Soils, Fertile Loamy Soils |
| Propagation Method | Seed |
Foliar
| Foliage Retention | Evergreen |
|---|---|
| Mature Foliage Colour(s) | Green |
| Mature Foliage Texture(s) | Glossy / Shiny, Leathery, Thick |
| Prominent Young Flush Colour(s) | Red |
| Young Flush Texture(s) | Leathery |
| Foliar Type | Simple / Unifoliate |
| Foliar Arrangement Along Stem | Opposite |
| Foliar Attachment to Stem | Petiolate |
| Foliar Shape(s) | Non-Palm Foliage (Oblong, Obovate) |
| Foliar Venation | Pinnate / Net |
| Foliar Margin | Entire |
| Foliar Apex - Tip | Acuminate, Acute |
| Foliar Base | Cuneate |
| Leaf Area Index (LAI) for Green Plot Ratio | 4.0 (Tree - Dense Canopy) |
Non - Foliar and Storage
| Mature Bark Texture | Cracked |
|---|---|
| Stem Type & Modification | Woody |
| Root Type | Underground (Tap Root) |
Floral (Angiosperm)
| Flower & Plant Sexuality | Unisexual Flowers , Dioecious |
| Flower Colour(s) | Red, Orange |
|---|
| Flower Grouping | Cluster / Inflorescence, Solitary |
| Flower Location | Terminal |
| Flower Symmetry | Radial |
| Individual Flower Shape | Cruciform / Cross-shaped |
| Inflorescence Type | Cyme, Raceme |
| Flowering Period | A Few Times Yearly |
| Flowering Habit | Polycarpic |
Fruit, Seed and Spore
| Mature Fruit Colour(s) | Orange, Yellow / Golden |
|---|---|
| Fruit Classification | Simple Fruit |
| Fruit Type | Fleshy Fruit , Berry |
References
| References | <1> Gardner, S., Sidisunthorn, P. & Chayamarit, K. (2015). Clusiaceae. Forest Trees of Southern Thailand, vol. 1, pp 348. Bangkok: Kobfai Publishing Project. <2> Ngernsaengsaruay, C. (2022). Lectotypifications of Three Names in Garcinia, Synonymy of Garcinia pedunculata and Detailed Descriptions of Three Species in Garcinia Section Brindonia (Clusiaceae), Diversity 14: 556. |
|---|
Image Repository
Others
| Master ID | 1630 |
|---|---|
| Species ID | 2923 |
| Flora Disclaimer | The information in this website has been compiled from reliable sources, such as reference works on medicinal plants. It is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment and NParks does not purport to provide any medical advice. Readers should always consult his/her physician before using or consuming a plant for medicinal purposes. |









-(5).jpg)
-(9).jpg)



